As acids/bases & ph worksheet answers take center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of chemical interactions, unveiling the fundamental principles that govern these fascinating substances. Acids and bases, with their distinct properties and profound impact on our world, are meticulously explored, providing a comprehensive understanding of their nature and applications.
Delving into the intricacies of the pH scale, we uncover the secrets of measuring acidity and basicity, unraveling the relationship between pH and the chemical behavior of solutions. The captivating world of acid-base reactions unfolds, revealing the dynamics of neutralization and the role of buffers in maintaining pH balance.
Acids and Bases: Acids/bases & Ph Worksheet Answers
Acids and bases are two fundamental chemical concepts that play a crucial role in various scientific disciplines. According to the Arrhenius theory, an acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while a base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
Acids generally have a sour taste, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and turn blue litmus paper red. Bases, on the other hand, have a bitter taste, feel slippery to the touch, and turn red litmus paper blue. Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and acetic acid (CH3COOH), while common examples of bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and ammonia (NH3).
pH Scale
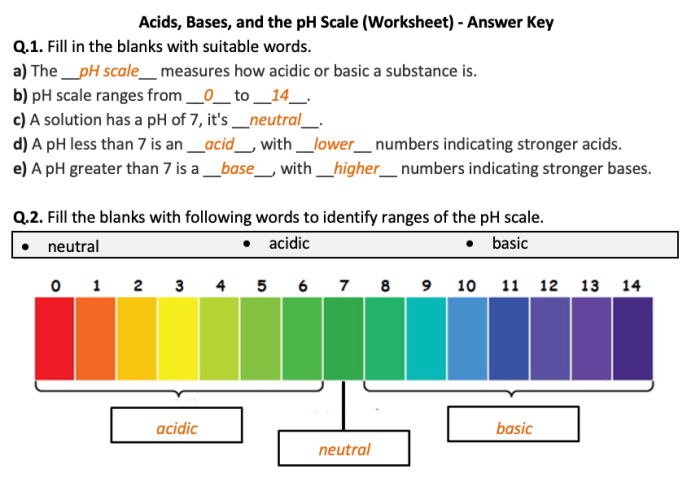
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Solutions with a pH below 7 are acidic, while solutions with a pH above 7 are basic.
The pH of a solution is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. The higher the concentration of hydrogen ions, the lower the pH and the more acidic the solution. Conversely, the lower the concentration of hydrogen ions, the higher the pH and the more basic the solution.
Acid-Base Reactions
An acid-base reaction is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base. The general reaction between an acid and a base can be represented as follows:
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), it produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O):
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
The reaction between an acid and a base is known as neutralization. During neutralization, the hydrogen ions from the acid combine with the hydroxide ions from the base to form water, resulting in a neutral solution.
Buffers, Acids/bases & ph worksheet answers
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH. They are composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. When a small amount of acid or base is added to a buffer solution, the buffer system reacts to neutralize the added acid or base, thereby minimizing changes in pH.
Buffers play a crucial role in maintaining pH balance in biological systems. For example, the bicarbonate buffer system in the blood helps to maintain a constant pH in the body, despite changes in the levels of carbon dioxide and other acids produced during metabolism.
Applications of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have numerous applications in everyday life, including:
- Industry: Acids are used in the production of fertilizers, plastics, dyes, and other chemicals. Bases are used in the production of soaps, detergents, and paper.
- Medicine: Acids are used as antiseptic and disinfectant solutions. Bases are used in the production of antacids and other medications.
- Agriculture: Acids are used as soil amendments to lower pH levels. Bases are used as fertilizers to increase pH levels.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
According to the Arrhenius theory, acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating basicity.
What is a buffer solution?
A buffer solution is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. Buffers consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.