Welcome to the ultimate guide to understanding the intricate processes of mitosis and meiosis, as captured in the activity mitosis and meiosis comparison answer key. This in-depth resource will illuminate the fundamental differences between these two vital cell division mechanisms, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of their significance in biology.
Prepare to delve into the fascinating realm of cell biology, where the secrets of life’s building blocks are unveiled. Through this journey, you will gain a profound appreciation for the precision and complexity that govern the very essence of existence.
Introduction
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that play crucial roles in the growth, development, and reproduction of organisms. Mitosis is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues, while meiosis is involved in sexual reproduction and the creation of gametes (eggs and sperm).
The key difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of daughter cells produced and the genetic makeup of those cells.
Phases of Mitosis
Mitosis consists of four distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, the chromosomes align at the equator of the cell. In anaphase, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
In telophase, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Prophase | Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelope breaks down |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles |
| Telophase | New nuclear envelopes form, cell divides into two daughter cells |
Phases of Meiosis: Activity Mitosis And Meiosis Comparison Answer Key
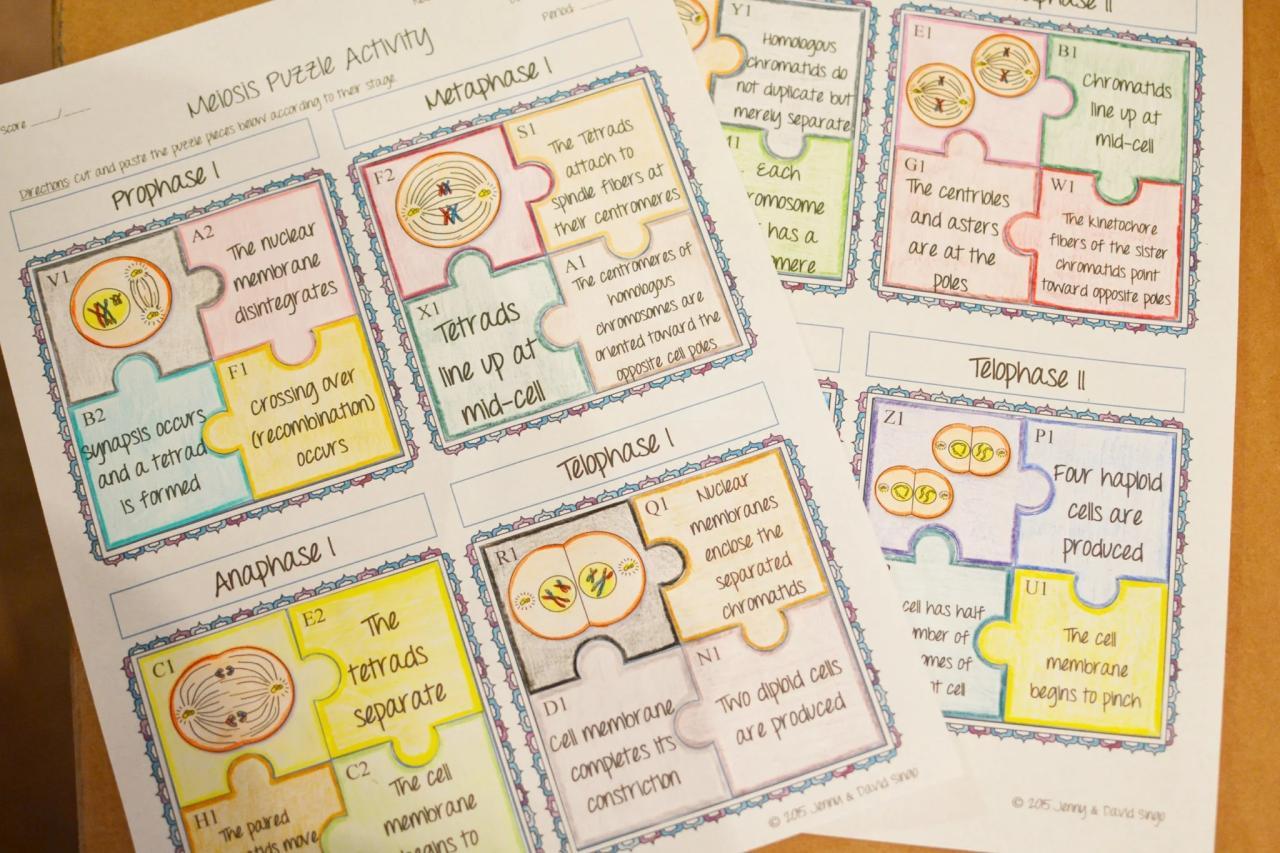
Meiosis consists of two rounds of division, known as meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, the chromosomes pair up and undergo recombination, resulting in the exchange of genetic material. The chromosomes then separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
In meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles, resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Meiosis I | Chromosomes pair up, undergo recombination, separate |
| Meiosis II | Sister chromatids separate, resulting in four haploid daughter cells |
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
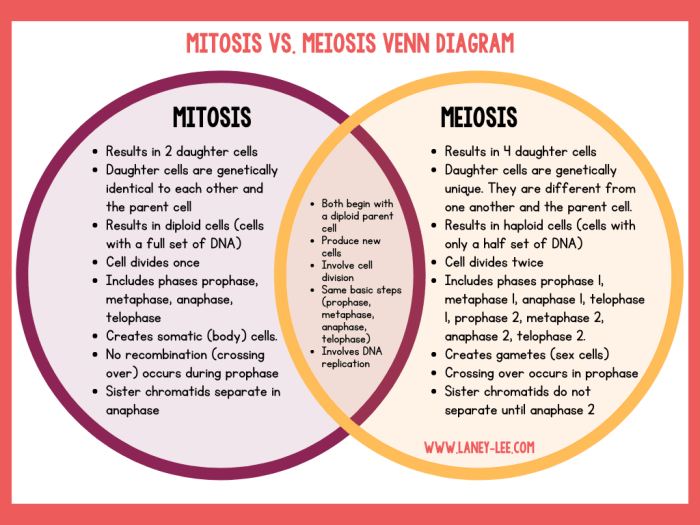
The key differences between mitosis and meiosis are summarized in the following table:
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Genetic makeup of daughter cells | Identical to parent cell | Haploid (half the number of chromosomes as parent cell) |
| Purpose | Growth, development, tissue repair | Sexual reproduction |
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of mitosis?
Mitosis plays a crucial role in growth, development, and tissue repair by producing genetically identical daughter cells.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
Meiosis shuffles genetic material during sexual reproduction, resulting in offspring with unique combinations of traits.
What are the potential consequences of errors in mitosis?
Errors in mitosis can lead to developmental abnormalities, genetic disorders, and cancer.