Compare and contrast the church system and feudal system – The comparison and contrast of the church system and feudal system embark on a historical expedition, delving into the intricate tapestry of two influential structures that shaped medieval society. From hierarchical organization to economic roles and cultural impact, this analysis unravels the similarities and distinctions between these two systems, shedding light on their profound impact on Western civilization.
The church system, rooted in religious authority, mirrored a hierarchical structure with the pope at its apex, while the feudal system, grounded in land ownership, established a decentralized network of lords and vassals. Both systems played significant economic roles, with the church collecting tithes and feudal lords levying taxes, yet their sources of power and influence diverged, with the church wielding spiritual authority and feudal lords exercising temporal control.
Hierarchical Structure
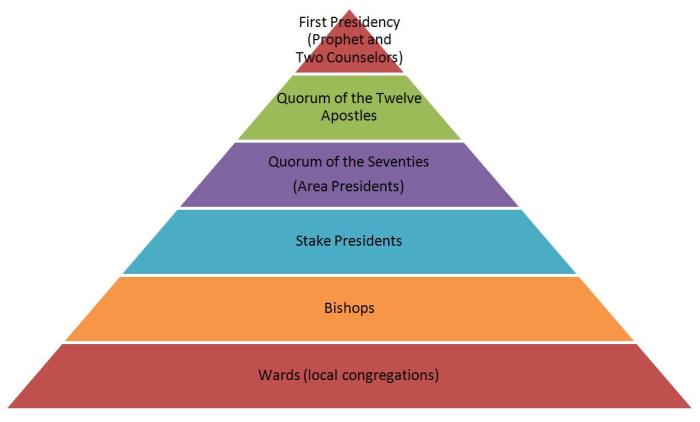
Both the church system and the feudal system featured a hierarchical structure, with different levels of authority and responsibility.
In the church system, the pope held the highest position, followed by cardinals, bishops, priests, and deacons. Each level had specific roles and responsibilities, such as administering sacraments, preaching, and providing spiritual guidance.
In the feudal system, the king or emperor was at the top of the hierarchy, followed by nobles, knights, and peasants. Nobles held land from the king and owed him military service in return. Knights were professional warriors who fought for the nobles.
Peasants were the lowest class and worked the land for the nobles.
The hierarchical structure of both systems influenced decision-making and power dynamics. In the church system, the pope had the final say on all matters of faith and morals. In the feudal system, the king had the ultimate authority to make laws and declare war.
Land Ownership and Control

Land ownership played a crucial role in both the church system and the feudal system.
In the church system, the church acquired land through donations from wealthy patrons and rulers. The church used its landholdings to generate income through agriculture, rents, and tithes (a tax on agricultural produce).
In the feudal system, land was the primary source of wealth and power. Nobles held land from the king and used it to support their households and raise armies. Peasants worked the land for the nobles and paid rent or taxes in return for protection and the right to use the land.
Land ownership gave the church and feudal lords significant power and influence. They could use their land to support their own interests, control the population, and raise armies.
Economic Roles: Compare And Contrast The Church System And Feudal System

The church and feudal lords played different economic roles.
The church primarily relied on tithes and donations for its income. Tithes were a tax on agricultural produce that all Christians were required to pay. The church also generated income through the sale of indulgences (pardons for sins) and the establishment of monasteries that engaged in agriculture and trade.
Feudal lords primarily relied on rent and taxes from their peasants for their income. They also engaged in agriculture, hunting, and trade. Some feudal lords also had the right to collect tolls and customs duties.
The economic power of the church and feudal lords allowed them to influence political and social policies.
Social Stratification
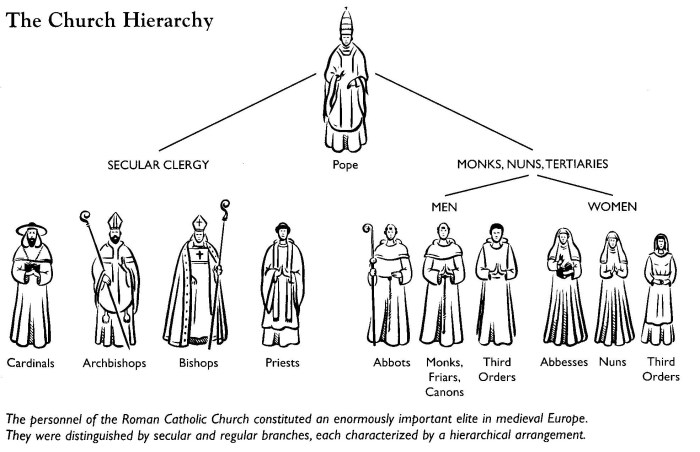
Both the church system and the feudal system featured social stratification systems.
In the church system, the clergy were at the top of the social hierarchy, followed by the nobility, then the common people. The clergy were seen as the spiritual leaders of society and were exempt from many taxes and obligations.
The nobility were the ruling class and owned most of the land. The common people were the lowest class and worked the land for the nobles or clergy.
In the feudal system, the social hierarchy was similar to that of the church system. The nobles were at the top, followed by the knights, then the peasants. The nobles owned most of the land and held all the political power.
The knights were professional warriors who fought for the nobles. The peasants were the lowest class and worked the land for the nobles.
Social stratification had a significant impact on the lives of individuals and the functioning of society.
Essential Questionnaire
What were the key differences between the church system and feudal system?
The church system was based on religious authority, with the pope as its head, while the feudal system was based on land ownership and a decentralized network of lords and vassals.
How did the economic roles of the church and feudal lords differ?
The church collected tithes, while feudal lords levied taxes. The church used its wealth to fund religious activities and support the poor, while feudal lords used their wealth to maintain their power and lifestyle.
What was the impact of the church system and feudal system on medieval society?
The church system and feudal system shaped the political, economic, and social structures of medieval society. They influenced everything from land ownership to social stratification to cultural norms.

