Label the figure showing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activation sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The significance of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) in the immune system cannot be overstated, and their activation plays a pivotal role in the body’s defense against pathogens.
This article delves into the intricate mechanisms of CTL activation, exploring the structural and functional aspects of these cells, the signaling pathways involved, and the cytotoxic mechanisms they employ to eliminate target cells.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Introduction
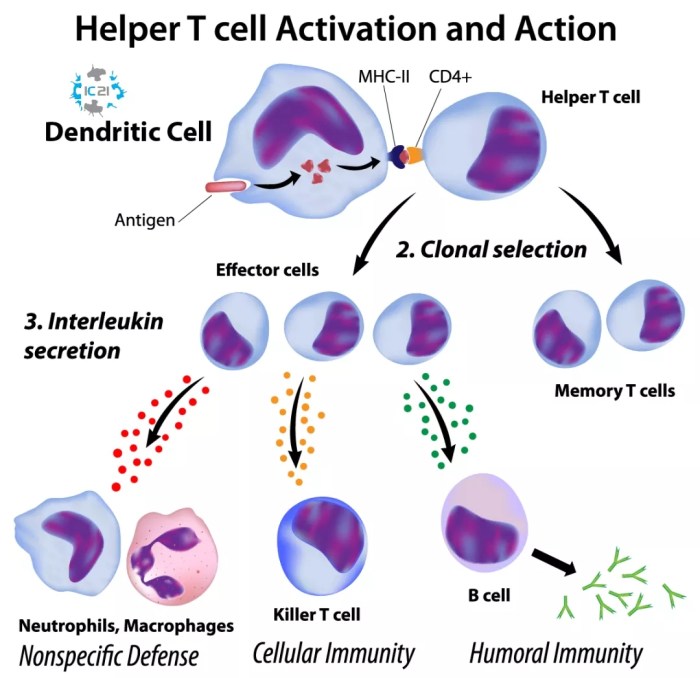
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) are essential components of the adaptive immune system, playing a critical role in the elimination of infected and cancerous cells. CTL activation is a complex process involving antigen presentation, co-stimulation, and cytokine signaling, leading to the development of cytotoxic effector cells capable of killing target cells.
Structure and Function of CTLs
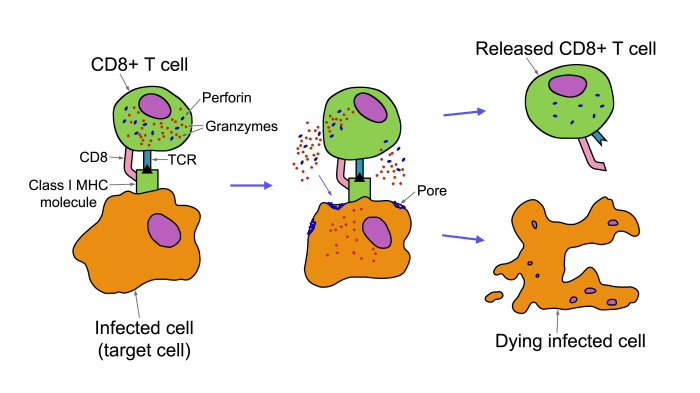
CTLs are a type of white blood cell characterized by the expression of the CD8 surface receptor. They recognize and bind to target cells presenting specific antigens on their MHC class I molecules. Upon binding, CTLs release cytotoxic molecules such as perforin and granzymes, leading to the apoptosis of the target cell.
Activation of CTLs
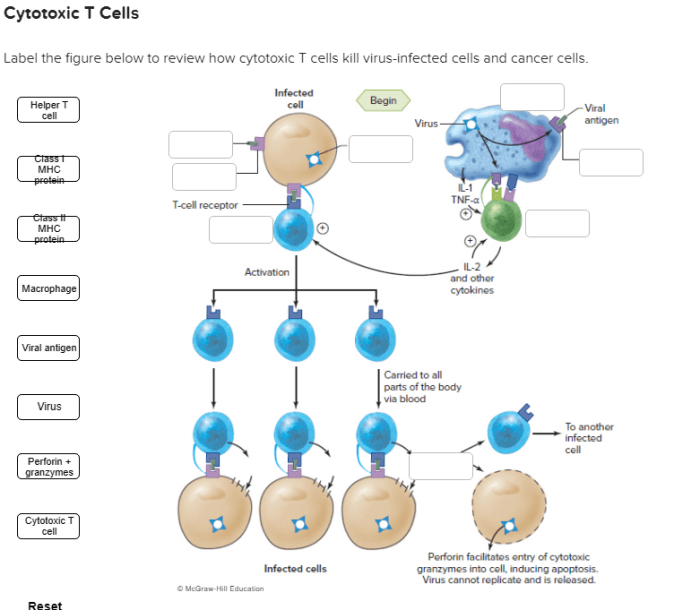
CTL activation involves several steps:
- Antigen presentation by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to the TCR on CTLs
- Co-stimulation by molecules such as CD28 on CTLs and B7 on APCs
- Cytokine signaling, particularly IL-2, which promotes CTL proliferation and differentiation
Cytotoxic Mechanisms of CTLs
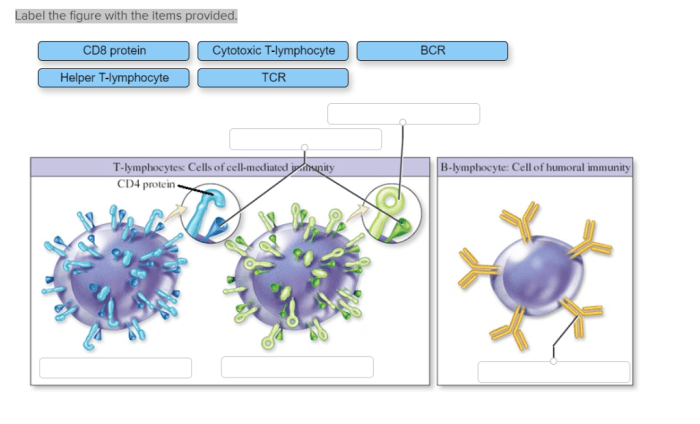
CTLs employ two main cytotoxic mechanisms:
- Fas-mediated apoptosis:CTLs express Fas ligand (FasL), which binds to Fas receptors on target cells, triggering apoptosis.
- Granzyme-mediated apoptosis:CTLs release granzymes, which enter target cells and activate caspases, leading to apoptosis.
User Queries: Label The Figure Showing Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Activation
What is the role of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes in the immune system?
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) are specialized immune cells that play a critical role in eliminating infected or cancerous cells. They recognize and bind to target cells, releasing cytotoxic molecules that induce apoptosis or cell death.
How are CTLs activated?
CTL activation involves a series of steps, including antigen presentation by antigen-presenting cells, co-stimulation by molecules such as CD28, and cytokine signaling. Cytokines like interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) play key roles in promoting CTL activation and proliferation.
What are the cytotoxic mechanisms used by CTLs?
CTLs employ two main cytotoxic mechanisms: Fas-mediated apoptosis and granzyme-mediated apoptosis. Fas-mediated apoptosis involves the binding of Fas ligand (FasL) on the CTL surface to Fas receptors on the target cell, triggering a signaling cascade that leads to cell death.
Granzyme-mediated apoptosis involves the release of granzymes from CTLs into the target cell, where they activate caspases and induce apoptosis.