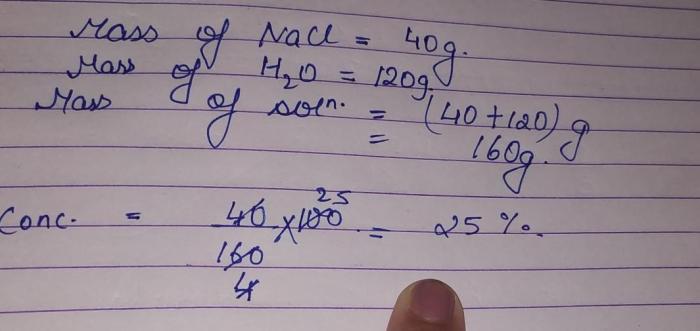Massing out 120g of sodium chloride requires a precise understanding of mass measurement, chemical properties, applications, safety considerations, and environmental impact. This guide delves into each aspect, providing a comprehensive overview of this essential compound.
Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is an ionic compound with a wide range of industrial and domestic applications. Understanding its properties and handling procedures is crucial for safe and effective use.
Mass Measurement and Conversion: Massing Out 120g Of Sodium Chloride

Precise mass measurement is crucial in chemistry. Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is a compound often used in various chemical experiments and industrial applications. Measuring its mass accurately is essential for obtaining reliable results.
Mass Measurement using a Weighing Scale
To measure 120g of sodium chloride, a weighing scale is typically used. Here’s a step-by-step process:
- Calibrate the weighing scale using a known weight to ensure accuracy.
- Place an empty container or weighing paper on the scale and press the “tare” button to zero out the scale.
- Gradually add sodium chloride to the container while observing the scale’s reading.
- Continue adding sodium chloride until the scale reaches 120g.
- Record the mass reading and transfer the sodium chloride to the desired container.
Mass Conversion
In scientific applications, it’s often necessary to convert mass measurements between different units. Here’s a table demonstrating the conversion of grams to other units of mass:
| Unit | Conversion to Grams |
|---|---|
| Milligrams (mg) | 1 gram = 1000 milligrams |
| Kilograms (kg) | 1 kilogram = 1000 grams |
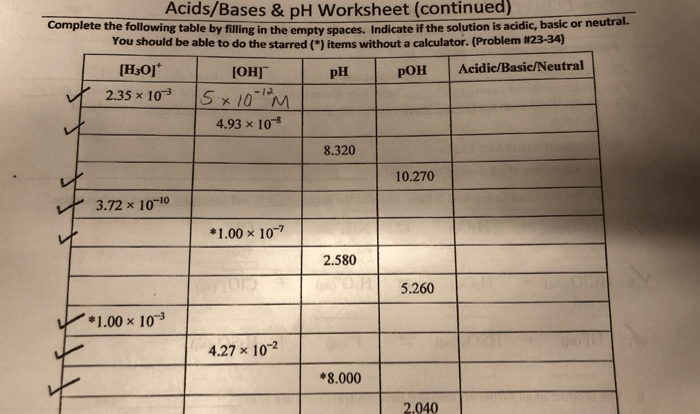
Chemical Properties of Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound with a strong ionic bond between sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions. It is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water.
Solubility
Sodium chloride is highly soluble in water due to its polar nature. The positive sodium ions are attracted to the negative oxygen atoms in water molecules, while the negative chloride ions are attracted to the positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules.
This attraction causes the sodium chloride to dissolve into water, forming a homogeneous solution.
Reactivity, Massing out 120g of sodium chloride
Sodium chloride is a relatively unreactive compound. It does not react with most other substances at room temperature. However, it can react with some metals, such as iron, to form rust.
Molar Mass
The molar mass of a compound is the mass of one mole of that compound. The molar mass of sodium chloride is 58.44 g/mol. This means that one mole of sodium chloride contains 58.44 grams of sodium chloride.
Molar mass of NaCl = 22.99 g/mol (Na) + 35.45 g/mol (Cl) = 58.44 g/mol
Applications of Sodium Chloride

Sodium chloride, commonly known as salt, is a versatile substance with numerous applications beyond its culinary use. It plays a crucial role in various industries, including food preservation, water treatment, and transportation.
In the food industry, sodium chloride is primarily used as a flavor enhancer and preservative. It inhibits the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms, extending the shelf life of food products. In addition, salt is used to cure meats, such as bacon and ham, imparting a distinctive flavor and texture.
Water Softening
Sodium chloride is employed in water softening systems to remove calcium and magnesium ions, which can cause water hardness. The process involves passing hard water through a resin bed containing sodium ions. The calcium and magnesium ions are exchanged for sodium ions, resulting in softened water.
Deicing Agent
Sodium chloride is extensively used as a deicing agent on roads and sidewalks during winter. It lowers the freezing point of water, preventing ice formation and ensuring safer driving conditions. However, excessive use of salt can damage vegetation and aquatic ecosystems, so its application must be carefully managed.
Safety Considerations
Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is generally safe to handle and consume in moderate amounts. However, certain precautions must be taken to ensure proper storage, disposal, and consumption.
When handling sodium chloride, it is important to wear gloves and a mask to prevent skin and respiratory irritation. Avoid direct contact with eyes, as it can cause irritation and discomfort. Store sodium chloride in a cool, dry place away from moisture and heat to prevent caking and contamination.
Disposal
Sodium chloride can be disposed of through regular waste disposal methods. However, large quantities of sodium chloride should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations to prevent environmental contamination.
Excessive Intake
Excessive consumption of sodium chloride can lead to several health risks, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. It is recommended to limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day, according to the American Heart Association.
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as kidney disease or hypertension, should consult with their healthcare provider for personalized sodium intake guidelines.
Environmental Impact
The production and use of sodium chloride can have significant environmental impacts. These impacts include:
Water Resources
The extraction of salt from seawater or underground salt deposits requires large amounts of water. This water is used to dissolve the salt and then to separate the salt from the water. The wastewater from this process can contain high levels of salt and other pollutants, which can contaminate water resources.
Ecosystems
The discharge of wastewater from salt production can also harm ecosystems. The high salt content of the wastewater can kill fish and other aquatic life. It can also damage vegetation and soil.
Strategies for Minimizing the Environmental Footprint of Sodium Chloride Use
There are a number of strategies that can be used to minimize the environmental footprint of sodium chloride use. These strategies include:
- Using more efficient salt production methods.
- Recycling salt.
- Using salt alternatives.
Detailed FAQs
What is the molar mass of sodium chloride?
The molar mass of sodium chloride is 58.44 g/mol.
What are the common applications of sodium chloride?
Sodium chloride is widely used as a food additive, water softener, deicing agent, and in various industrial processes.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling sodium chloride?
Sodium chloride should be stored in a cool, dry place and handled with care to avoid ingestion or inhalation.
What is the environmental impact of sodium chloride production and usage?
Sodium chloride production and usage can impact water resources and ecosystems, highlighting the need for responsible use and disposal.